What Are the Main Types of Server Chassis and Rack Units
A server chassis keeps all the main server parts safe. It holds things like the motherboard, drives, and power supply. A rack unit, called "U," shows how tall a server chassis is. It also shows the height of rack units. Server chassis and rack units are important. They make it easy to set up servers. They help with managing servers well. They also let you add more servers later. Most data centers use different racks. These are open frame racks, enclosed racks, wall mount racks, and OCP racks.
Server Chassis / Rack Type | Description | Height (rack units, U) | Key Features |
Open Frame Racks | Open design, basic support | Varies | Good airflow |
Enclosed Racks | Lockable, enclosed | 42U, 45U, 48U | Security, cable management |
Wall Mount Racks | Compact, wall-mounted | Up to 12U | Space-saving |
OCP Racks | Modular, efficient | 48U | Wider, modular design |
Key Takeaways
· Server chassis keep all server parts safe and neat. They also help cool the server and make it quieter.
· Rack units (U) show how tall a server is. They make sure equipment fits together for easy stacking and upgrades.
· There are different server chassis types like rackmount, tower, blade, GPU, and storage. Each type works best for certain jobs.
· Picking the right rack size and chassis type saves space. It also helps with cooling, safety, and future growth.
· Good cable management and airflow stop servers from getting too hot. They also make fixing things easier.
· Planning for more hardware later helps server rooms grow well. It also saves money over time.
· Better cooling and energy-saving designs help servers last longer. They also lower power bills.
· You can add things like locks and cooling to server cabinets. This keeps servers safe and helps them work better.
Server Chassis and Rack Units
Server Chassis Overview
A server chassis is the main frame for a server. People also call it a case or enclosure. It keeps all the parts safe and in order. The chassis is very important for any server.
The main jobs of a server chassis are:
1. Structure: The chassis holds all the parts together. This makes building and fixing the server easier.
2. Protection: The chassis keeps out dust, dirt, and water. It also blocks other things that could hurt the server.
3. Cooling: The chassis lets air move around inside. Good airflow helps keep the server cool.
4. Noise Reduction: The chassis can make the server quieter. It blocks some of the noise from fans and moving parts.
5. Aesthetics: The chassis makes the server look neat and nice. Some come in black, white, or gold.
Inside the server chassis are the motherboard, drives, power supply, and fans. There are sometimes extra slots for more hardware. All these parts fit inside the chassis. This makes it easy to upgrade or fix the server.
Tip: Picking the right server chassis helps you manage your server better. It also makes it easier to add or change parts later.
Rack Units Defined
A rack unit, or "U," is a way to measure how tall equipment is in a rack. One rack unit (1U) is 1.75 inches tall. The Electronic Industries Association made this standard. It helps all server equipment fit in racks.
Racks have rails with holes spaced for rack units. This lets you stack servers and other devices neatly. Most racks are 19 inches wide. The depth can be different for each rack.
Rack units help data centers plan how many servers fit in a rack. They make it easy to add or move equipment. The standard size means different brands can fit in the same rack.
Note: Rack units help you manage servers by making upgrades and changes quick. They also help with cooling, cable management, and security.
Server chassis and rack units are very important for setting up and running servers. They let you:
· Add more servers to the same rack easily.
· Get better airflow and cooling to keep parts safe.
· Keep cables neat so you can fix problems faster.
· Lock racks to keep equipment safe.
· Make upgrades and repairs simple, saving time and money.
Modern data centers use server chassis and rack units to work well. The right choices help with space, power, and cooling. This makes sure servers last longer and work better.
Types of Server Chassis

Rackmount
Rackmount server chassis are used a lot in data centers. They fit into racks and use space well. Each rackmount case has a height measured in rack units. The size can be 1U, 2U, or even 10U. You can stack many servers in one rack. This makes it easy to add or upgrade servers. Rackmount server chassis have slots for extra hardware. You can add network cards or storage drives. They also help keep cables neat and tidy.
A rackmount case is small and easy to stack. Many companies pick rack servers to save floor space. They let you put lots of servers in one place. But these chassis need good cooling. The parts are close together, so airflow is important. This stops the servers from getting too hot. Rackmount server chassis are good for companies that want to grow fast or have many servers in one spot.
Tip: Rackmount server chassis are great for saving space and making maintenance easy.
Tower
Tower server chassis look like big desktop computers. These are best for small offices or businesses with few servers. Tower chassis are simple to use and often cost less. They are bigger in size but have fewer parts inside. This means they do not need as much cooling as rackmount server chassis.
A tower server chassis gives you more space for upgrades. You can add more drives or memory if needed. These chassis are quieter and can fit under desks. They are good for small server rooms. Tower server chassis are not the best for big data centers. But they work well for small spaces or a few servers.
Note: Tower server chassis are a simple and cheap way to start using servers.
Blade
Blade server chassis are very compact and modular. They hold many thin server blades in one case. Each blade is its own server. They share power, cooling, and networking inside the chassis. Blade server chassis are best for places where space and power are important.
Blade server chassis let you add or remove blades easily. This makes upgrades and repairs quick. Blade chassis get hot, so they need strong cooling systems. Big companies use blade server chassis for data clusters and cloud computing. They give a lot of power in a small space.
Server Chassis Type | Distinguishing Features |
Rackmount Server | Small, stackable; saves space; can add hardware; needs good cooling; easy cable management. |
Tower Server | Looks like a desktop; easy to use; less cooling needed; costs less; not as dense. |
Blade Server | Modular and compact; holds many blades; easy to swap; needs strong cooling. |
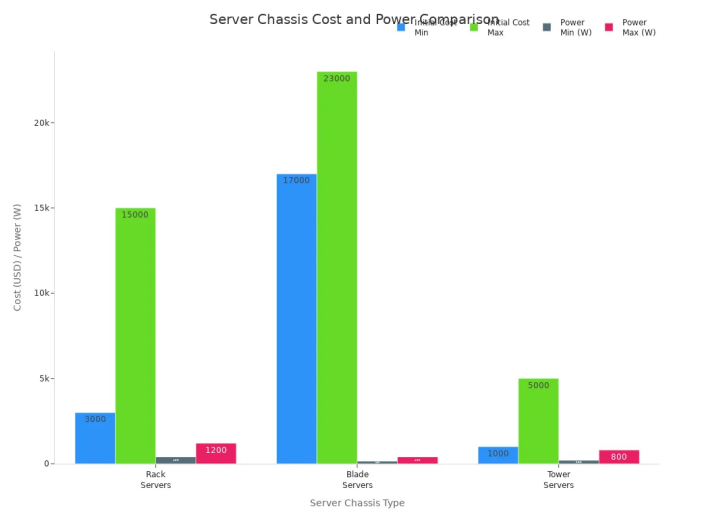
These three types of server chassis—rackmount, tower, and blade—meet most needs in IT today. Each type has special benefits for different server setups.
GPU
GPU server chassis are made for jobs that need strong graphics. These chassis can hold one or more GPUs inside. Many companies use GPU server chassis for artificial intelligence and machine learning. They also use them for video rendering. The chassis must fit big GPUs and give extra cooling. This helps the server work well when it is busy.
A GPU server chassis often has a special design. The design lets air move better around the GPUs. Some GPU chassis use more fans or liquid cooling to keep things cool. The server chassis also needs strong power supplies. GPUs use more power than other server parts.
Tip: GPU server chassis help make jobs faster when you need quick graphics or data work.
Many data centers use GPU server chassis for research and big data. They also use them for cloud gaming. These chassis make it easy to add or change GPUs. This helps the server stay new with better technology. Shenzhen Xintongtai Technology Co., Ltd. sells GPU server chassis for many needs. Their products work with high-end GPUs and have good cooling.
Storage
Storage server chassis are built to hold lots of drives. These chassis help companies keep lots of data safe. A storage server chassis has many drive bays in the front. This makes it easy to add or take out drives.
There are different kinds of storage server chassis. Some are small and hold just a few drives. Others are big and can hold many drives. The chassis must keep the drives cool and safe. Good airflow is important in a storage server chassis. Many storage chassis use fans or vents.
Storage Server Chassis Features | Description |
Drive Bays | Hold many drives for more storage |
Hot-Swap Support | Change drives without turning off the server |
Redundant Power | Extra power supplies for safety |
Cooling | Fans and vents to keep drives cool |
Storage server chassis help with backup and file sharing. They also help with cloud storage. Companies use these chassis to keep data safe and easy to get. Shenzhen Xintongtai Technology Co., Ltd. makes storage server chassis like the XTT465-36 and XTT415S48. These models give strong storage for many uses.
Other Types
Some server chassis are made for special jobs. Wallmount chassis save space by hanging on walls. ITX chassis are small and fit in tight places. Open frame chassis have no sides or doors. This makes it easy to fix or test parts. Pedestal chassis stand up like a tower but hold more parts. Edge server chassis work close to users at the edge of networks.
Note: Picking the right types of server chassis helps companies match their server to the job.
Shenzhen Xintongtai Technology Co., Ltd. has many kinds of server chassis. Models like XTT660H-T3E and XTT316H-T3 fit different jobs. Their server chassis work for data centers and small offices. The right chassis helps the server work better and last longer.
Understanding Rack Units

1U, 2U, 4U
Understanding rack units helps people plan and organize server spaces. A rack unit, or U, measures the height of equipment in a rack. One U equals 1.75 inches. This standard size lets different servers fit together in the same rack. A 1U server stands 1.75 inches tall and 19 inches wide. The depth can reach up to 23 inches. This small size means data centers can fit many 1U servers in one rack. High server density saves space and lowers power use.
A 2U server is twice as tall as a 1U server, measuring 3.5 inches in height. It still fits the 19-inch width. The 2U server gives more room for extra hardware, like more drives or bigger fans. A 4U server stands 7 inches tall. This larger size supports even more powerful parts or extra storage. Choosing between a 1U server, 2U server, or 4U server depends on the needs of the data center. Smaller units allow more servers in one rack, while larger units offer more features per server.
Tip: Using the right size server helps balance space, power, and cooling in a data center.
EIA Standards
The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) created the EIA-310 standard. This standard sets the rules for rack server cabinets. The EIA-310 standard defines the 19-inch width for racks. Each rack has two vertical metal posts, each 0.625 inches wide. The posts stand 19 inches apart. Holes in the posts follow a repeating pattern every 1.75 inches, which matches one U. The holes have a set spacing: 0.5 inches, 0.625 inches, and 0.625 inches. This pattern repeats for each rack unit.
Aspect | Definition / Measurement |
EIA-310 Standard | Standardizes 19-inch rack cabinet features, including front panel width, hole spacing, and rack unit height. |
Front Panel Width | Exactly 19 inches wide. |
Vertical Hole Spacing | Pattern within one U of 1.75 inches height; hole spacing alternates 1/2", 5/8", 5/8". |
Horizontal Spacing | Distance between vertical hole rows is about 18.3 inches. |
Rack Opening | Minimum opening is 17.72 inches for 2-post racks. |
Rack Unit (U) Height | Defined as 1.75 inches. |
Compliance | EIA-310 is widely followed for compatibility. |
The EIA-310 standard makes sure all server equipment fits together. This helps companies mix and match different brands and types of servers in one rack.
Server Capacity by Units
Server capacity depends on the number of rack units in a cabinet. A standard rack often holds 42U. Using 1U servers, a rack can fit up to 42 servers. This setup gives high density and saves floor space. A 2U server takes up twice the space, so only 21 servers fit in the same rack. A 4U server uses even more space, allowing only 10 servers per rack. Smaller units like the 1U server help maximize the number of servers in a rack. This increases computing power without using more space.
· High-density racks use 1U servers to pack more computing power into a small area.
· 2U servers and 4U servers offer more room for upgrades but reduce the total number of servers per rack.
· Choosing the right mix of server sizes helps balance performance, cooling, and energy use.
· Standard rack units make it easy to plan layouts and upgrade equipment.
Understanding rack units lets data centers design flexible and efficient server layouts. The right choices improve cooling, save energy, and make future upgrades simple.
Server Cabinets
19-Inch Cabinets
A 19-inch cabinet is used a lot in server rooms. It has a mounting width of 19 inches. Most servers and network gear fit this size. The 19-inch width lets you use different brands together. This makes it easy to mix equipment in one rack. Many cabinets use this width because of the EIA standard. The width helps mount servers and switches safely. The outside of these cabinets is often 24 inches wide. This matches the size of floor panels in data centers. It makes planning and setting up easier.
Tip: A 19-inch cabinet saves space and keeps things neat. This is a big reason to use a server rack.
42U Cabinets
A 42U cabinet is common in big companies. "U" means rack unit, and 1U is 1.75 inches tall. A 42U cabinet is about 6 to 7 feet high. This gives room for many servers and other gear. Companies pick 42U cabinets to balance space and how much they can hold. These cabinets are strong and can hold heavy equipment. Many have locking doors and side panels. Some let you add power units without tools. The doors often have holes to help with cooling. Some brands, like Lenovo and Vertiv, make deeper cabinets for cables and airflow. The 42U cabinet is good for growing and keeping things safe.
Cabinet Feature | Description |
Height | 42U (about 73.5 inches) |
Mounting Width | 19 inches (standard for most server equipment) |
Depth | Ranges from 29 to 48 inches, allowing for large servers and cable management |
Security | Locking doors and panels |
Cooling | Perforated doors, airflow channels, and space for fans |
Cabinet Dimensions
Cabinet size is important when setting up servers. The main sizes are height, width, and depth. Height tells you how many devices fit in the rack. Common heights are 42U, 48U, and smaller ones like 22U or 27U. Width is usually 19 inches for mounting. The outside width can be 24 inches. This extra width lines up with floor tiles and helps with cables. Depth can be 24 inches for network racks or up to 48 inches for deep cabinets. Deeper cabinets fit bigger gear and help air move better.
· Cabinet size helps with cooling by giving space for air and fans.
· The right depth and width make it easier to manage cables.
· Filling cabinets about 75-80% and leaving gaps helps cooling.
· Blank panels in empty spots stop hot and cold air from mixing.
The right cabinet size makes sure all gear fits and stays cool. Good planning helps keep things neat, easy to fix, and cool.
Customization
Every server room is different. Custom cabinets help meet these needs. Companies often change cabinet designs to fit their space. Some rooms are small or shaped oddly. A custom cabinet can fit in these places.
Some cabinets need special features for tough areas. Waterproof cabinets keep water out. Shockproof cabinets protect from bumps. Dustproof cabinets stop dust from getting inside. These features help keep servers safe and working.
Many people want better cable management. Custom cabinets can have extra holes or trays for cables. This keeps cables neat and easy to find. Good cable management helps air move better. Airflow is important for cooling. Some cabinets have special fans or vents for this.
Security is another reason to customize. Some cabinets have stronger locks or alarms. This keeps equipment safe from theft. Some companies need cabinets that follow certain rules. Custom cabinets can be made to meet these rules. This helps with safety and legal needs.
Here are some common ways to customize a server cabinet:
· Change the size or shape to fit special spaces or equipment.
· Add waterproof, shockproof, or dustproof features for tough environments.
· Improve cable management with trays, hooks, or extra holes.
· Add better locks, alarms, or security panels.
· Use special fans, vents, or airflow paths for cooling.
· Make sure the cabinet meets industry standards or certifications.
Tip: Plan for customization early to avoid problems later. This makes sure the cabinet works well for many years.
A custom cabinet gives more control over the server room. It helps keep equipment safe, cool, and easy to manage. Companies can pick the features they need most. This makes the cabinet a better fit for their work.
Server Deployment and Scalability
Space Efficiency
Space efficiency is important when setting up servers. Different server chassis use space in their own ways. Tower servers need the most room because they stand alone. These are best for small offices or places with few servers. Rack-mounted chassis let you stack servers on top of each other. This saves floor space and keeps things tidy. Blade server chassis fit many blades in one case. They share power and cooling. This design puts more computing power in less space.
Server Type | Form Factor & Deployment Style | Space Efficiency in High-Density Deployments |
Tower Servers | Standalone, larger units; suitable for small to medium deployments or where rack mounting is not feasible | Least space efficient due to larger size and standalone design |
Rack-mounted | Designed for standard racks (1U or 2U), stacked vertically | More space efficient by enabling vertical stacking in racks |
Blade Servers | Modular, smaller than rack-mounted; multiple blades share chassis resources (power, cooling, networking) | Most space efficient; very high-density computing in a single chassis |
Blade server chassis help data centers put more servers in one rack. This boosts performance and lets you add more servers without using more floor space. Rack-mounted chassis also help keep cables neat and easy to manage. Using space well helps air move better and keeps servers cool. This makes servers last longer and work better.
Hardware Expansion
Hardware expansion means you can add new parts later. Modular server chassis make upgrades easy. Rack servers let you add more servers to the rack when needed. Blade chassis let you slide in new blades fast. This saves time and keeps servers running.
Here are some best ways to expand hardware:
1. Plan where each piece of equipment will go.
2. Put heavy chassis at the bottom for safety.
3. Set rails at the right height.
4. Add equipment from the bottom up.
5. Use the right screws to hold each chassis.
6. Keep cables neat so air can move.
7. Use blank panels to help cooling and stop dust.
8. Plug equipment into grounded power units.
9. Label all equipment and cables.
10. Test everything to make sure it works well.
Blade server chassis make upgrades simple and quick. You can swap blades without turning off the whole chassis. Rack-mounted chassis let you use different server types in one rack. Good planning helps the server room stay ready for new needs.
Power and Cooling
Power and cooling are important for server health. Each server chassis makes heat. The total heat from all servers in a rack shows how much cooling you need. Blade chassis and racks with lots of servers get hotter. These need strong cooling to keep working well.
Good airflow is very important. Servers pull cool air from the front and push hot air out the back. Cabinets should have doors with lots of holes for air. Leave at least 1.5 inches of space for air to move. If air cannot move, servers get too hot and may not work right.
Power needs change with each chassis type. Blade server chassis share power supplies, which can save energy. Rack-mounted chassis use their own power for each server. Extra power supplies and backup power help if the power goes out. Data centers must check power and cooling for each rack, not just the whole room.
Managing power and cooling well keeps servers running smoothly. It also saves money and helps you add more servers later. Planning ahead makes sure each chassis works its best and stays reliable.
Real-World Scenarios
Many groups have different problems when setting up servers. Picking the right server chassis and rack units helps a business grow. It also helps them change when they need to. Here are some examples that show why these choices matter:
Data centers with little space often pick blade server chassis. Blade servers are thin and fit together in one case. This design lets you put many servers in a small area. For example, a 10U blade chassis can hold up to 16 blades. This saves floor space and makes it easy to add more power later. Blade chassis also put power, cooling, and networking in one place. This means fewer cables and easier management.
Cloud companies like AWS and Microsoft Azure use blade server chassis. They need to add or remove servers fast when things change. Blade servers let them do this without turning off everything. Special software helps watch all the blades and share resources. This way, they can grow quickly and keep things running well.
Science labs, like CERN, use blade servers for strong computing. These places need powerful servers in small spaces. Blade chassis give good cooling and power to each blade. This helps save energy and money. The modular design lets them add more blades for extra power. They do not need to change the whole setup.
Some businesses like rack servers for their flexibility. Rack servers stand alone and have their own power and cooling. Companies can add one server at a time for small upgrades. This is good for small offices or places with more room. Rack servers can be changed more, but they use more space.
Security matters in shared or open places. Standard racks cost less and are easy to set up. But they may not protect enough. Secure server enclosures keep equipment safe from theft or damage. They also help with airflow and cable management. Some groups use both secure enclosures and standard racks. This mix saves money, keeps things safe, and helps with future growth.
Tip: The right chassis and rack units can save money, boost security, and make growing easier.
These examples show that good planning and hardware choices help a business grow. Picking the right setup lets companies change, grow, and keep their data safe.
Server Room Best Practices
Chassis and Rack Selection
Picking the right server chassis and rack units is very important. You need to think about the room size and how many servers you want. The type of equipment also matters. A good server chassis keeps hardware safe and cool. Racks help keep servers and cables neat and tidy.
When choosing a server chassis, look at these things:
· How many rack units you need for all your equipment.
· What type of chassis fits your space and future plans.
· How much cooling and power each chassis needs.
· Security features like locks or cameras for safety.
· The room’s temperature and humidity control.
· Modular racks that make it easy to add more later.
A table can help you compare what matters most:
Factor | Why It Matters |
Rack Size | Holds all your servers now and later |
Chassis Type | Fits your space and upgrade plans |
Cooling | Stops servers from getting too hot |
Security | Keeps equipment safe from harm |
Cable Management | Stops mess and helps air move |
Tip: Always think about what you might need in the future when picking server chassis and racks.
Configuration Mistakes
People often make mistakes when setting up servers. These mistakes can cause overheating or even break equipment. Some common mistakes are blocking airflow, putting heavy things too high, and messy cables.
To stop these problems, follow these steps:
· Put heavy things like UPS units at the bottom for safety.
· Use the right screws and cage nuts for each chassis.
· Set up racks in hot and cold rows to help cooling.
· Do not put too many servers in one rack.
· Label all equipment and cables and keep records.
· Keep cables neat so air can move around.
· Watch the temperature and humidity in the room.
· Use power units to stop power overloads.
Note: Good planning and careful setup can stop most problems before they start.
Cable Management
Cable management in server racks is very important. Messy cables can block air and make things too hot. They also make fixing things harder. Good cable management keeps everything neat and easy to reach.
Here are some best ways to manage cables:
· Use cable managers to keep cables straight and tidy.
· Bundle cables with velcro ties so you can change them easily.
· Use colors and labels to find cables fast.
· Keep power and data cables apart to stop problems.
· Leave space between servers for better airflow.
· Put blank panels in empty spaces to guide air.
· Keep walkways clear for people and equipment.
Tip: Write down all cable connections and update your notes when you make changes. This makes fixing and upgrading much easier.
Scalability Planning
Scalability planning helps a server room grow with new tech. Good planning makes it easy to add servers or upgrade gear. Here are some simple steps for smart scalability planning:
1. Build the server room so it can grow. Use modular racks and cabinets for easy upgrades. This lets teams add servers or storage without moving everything.
2. Pick routers, switches, and cables that hold lots of data. These parts can handle more as the network gets bigger. Strong parts help avoid early replacements.
3. Use new network tools like SDN and cloud-native systems. These tools help manage the network and make changes faster.
4. Add security that grows with the network. Use zero trust to keep data safe as more devices connect.
5. Check how the network works often. Look for slow spots or problems. Fixing these early keeps things running well as it grows.
6. Use automation and AI to manage network resources. These tools help change settings fast and need less manual work.
7. Pick modular and compatible parts. This makes it easy to add new tech or expand without big changes.
8. Work with experts and trusted partners. They help set up systems that are easy to grow and keep costs low.
Tip: Planning for scalability early saves time and money. It also helps the server room get ready for new needs.
A good plan helps the server room handle more users and data. Teams can add equipment or upgrade without big changes. This keeps the network strong and flexible for a long time.
Innovations in Server Cooling and Design
Modular Chassis
Modular chassis have changed how data centers work. Each node in these chassis has compute, memory, storage, and network parts. This design lets you add or remove nodes when you need to. Many companies like modular chassis because they are easy to set up and upgrade. Hyper-converged infrastructure uses modular chassis to put all main server parts together. This helps edge computing and hybrid cloud systems grow. Modular chassis help save money and make servers easier to manage. They also keep the system running if one part breaks. You can make the system bigger by adding more nodes. This makes it faster without making things harder. These chassis also cut down on extra parts, so the server room is less crowded and easier to take care of.
Modular chassis help virtual desktop infrastructure by giving each desktop the right resources. This makes the system flexible and ready to grow.
Advanced Cooling
Advanced cooling is important for keeping server chassis safe. Powerful servers make more heat. Good cooling keeps them working well and stops damage. Many data centers now use liquid cooling and better airflow. These ways cool servers faster and use less energy than old systems. Liquid cooling moves heat away from hot parts quickly. This helps servers last longer and work better.
Shenzhen Xintongtai Technology Co., Ltd. is a leader in advanced cooling. Their XTT-10 CPU cooler keeps CPUs safe, even when working hard. This cooler moves heat away from the processor to keep it steady. The company also makes power supplies and heatsinks. These parts work together to keep servers cool and running well.
Advanced cooling protects server parts and helps them work their best.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is now very important in server chassis design. Energy-efficient chassis use smart airflow and support liquid cooling. These designs lower the power needed to keep servers cool. When servers use less energy, they make less heat. This means cooling systems do not have to work as hard. This saves money and helps the environment.
Modern chassis use power supplies that waste less energy and low-power parts. These features help hardware last longer. Multi-node chassis need fewer extra parts, so they use less energy. Smart fan controls and energy-saving CPUs and memory also help lower power use. These steps let you add more servers without raising costs too much.
Energy-efficient chassis help data centers save money, protect the planet, and keep servers working well.
Knowing about server chassis and rack units helps groups build strong server rooms. These choices change how much space and energy the server room uses. Teams can use small rack units to fit more servers in one spot. Bigger chassis give more power for special jobs.
· Planning well makes it easy to upgrade servers and keeps them safe.
· Good airflow and neat cables help stop servers from breaking.
· Modular designs let you add more servers and fix them easily.
· Different chassis types help each server do its job best.
· Strong server setups keep data safe and let work keep going.
· Making smart choices now helps server rooms grow in the future.
FAQ
What is a server chassis?
A server chassis is the main frame that holds all server parts. It protects the motherboard, drives, and power supply. The chassis also helps with cooling and keeps everything organized.
How tall is a 1U server?
A 1U server measures 1.75 inches in height. This size fits into standard 19-inch racks. Data centers use 1U servers to save space and stack more servers in one cabinet.
Why do data centers use rack units?
Rack units help data centers organize and plan server space. Each rack unit (U) gives a standard height. This makes it easy to fit different servers and equipment together.
What is the difference between rackmount and tower servers?
Feature | Rackmount Server | Tower Server |
Shape | Flat, stackable | Tall, upright |
Space Use | Saves space | Needs more room |
Best For | Data centers | Small offices |
Can you mix different server chassis in one rack?
Yes, as long as each chassis follows the same rack unit standard. Most racks use the 19-inch width and standard U heights. This lets users mix brands and types in one rack.
How does cooling work in server racks?
Fans pull cool air from the front and push hot air out the back. Good airflow keeps servers from overheating. Some racks use extra fans or special coolers for better results.
What should you check before buying a server cabinet?
· Cabinet height and width
· Cooling features
· Cable management options
· Security locks
· Room for future upgrades
These checks help users pick the right cabinet for their needs.
